During the design of a bearing assembly, the topic of sealing will always accompany you. In the following material, we will cover both integrated and external sealing concepts. Both are used to prevent lubricant from escaping and to prevent contaminants (such as dust and water) from entering the rolling bearing.
Sealing variants for rolling bearings
Integrated seals are integrated into the rolling bearing and pressed into the inner or outer ring. Integrated seals are mainly used in deep groove ball bearings. External seals, on the other hand, must be planned during the design phase. They are used in bearing types where no integrated seal is provided (mainly in roller bearings) or if an integrated seal is not sufficient and the bearing still needs additional protection. The functions of integrated and external seals are identical.
Certain factors should be taken into account when choosing a seal. These include the type of lubricant, the circumferential speed at the seal lip, fitting errors of the shaft, spatial limitations, the seal friction and the associated temperature increase. The seal material also plays an important role in the choice of seal. Of course, the costs incurred must also be considered.
Integrated seals
The integrated seals can be divided into different types, some of which are defined in more detail in this section. All seals listed below are used for dust protection and sealing on both sides. The main integrated seals of rolling bearing manufacturer NTN are the seals ZZ, LLB, LLU and LLH (with low frictional torque).
| Type, designation | Version with metal shield | Version with elastomer seal | ||||||||||||
| Non-contact shield ZZ | Non-contact seal LLB | Contact seal LLU | Contact seal LLH with low friction torque | |||||||||||
| Design | 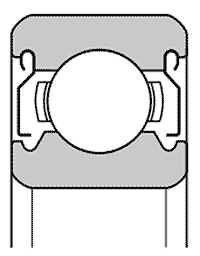 | 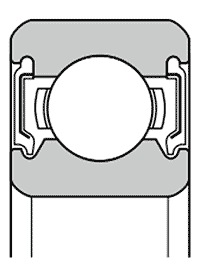 |  | 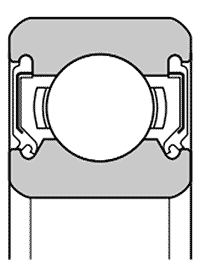 | ||||||||||
| – A metal plate shield is located in outer ring groove; a V-groove with a labyrinth gap runs in the inner ring | – A rubber-moulded pressed steel plate is clipped into the outer ring; the sealing lip runs close to the inner lip in the V-groove, but without contact | – A rubber-moulded pressed steel plate is clipped into the outer ring; the inner sealing lip touches the V-groove on the inner lip | – The basic design is the same as LLU, but the contact of the inner sealing lip is reduced. This results in a lower frictional torque | |||||||||||
| Performance comparison | Frictional torque | Low | Low | Relatively high | Relatively low | |||||||||
| Dust tightness | Very good | Better than ZZ | Excellent | Much better than LLB | ||||||||||
| Waterproofness | Bad | Bad | Very good | Very good | ||||||||||
| Permissibility of high speeds | Like open type | Like open type | Limited by circumferential speed | Higher than LLU | ||||||||||
| Permissible temperature range | Depends on the lubricant | -25 °C ~ 120 °C | -25 °C ~ 110 °C | -25 °C ~ 120 °C | ||||||||||
Here are examples of integrated seals for ball bearings and their design and properties.
External seals
Unlike integrated seals, external seals are not integrated into the rolling bearing and must be added separately. They can be divided into two types, namely non-contact seals and contact seals.
Non-contact seals
The most important feature of non-contact seals is that in this variant there is a small gap, or labyrinth, between the seal and the rotating part. Seals of this type are suitable for high-speed applications as there is no high seal friction. In addition, oil or grease is usually applied to any remaining gaps to provide improved sealing capability.
Examples of non-contact seals
In general, lubrication (oil or grease) between the contact point of the sealing lip and the inner or outer ring of the bearing is indispensable. In the case of oil lubrication, suitable sealing concepts are required that prevent oil leakage during operation. In addition, the most important seal designs, their properties and other criteria for choosing the right seal can be found in the following tables.
| Non-contact seals | ||
| Seal structure | Designation | Sealing properties, design criteria |
 | Gap seal |
|
 | Gap seal with oil grooves at the housing opening |
|
 | Labyrinth seal (axial example) |
|
Relevant examples of non-contact seals are the gap seal and the labyrinth seal.
Labyrinth seal
While the gap seal is considered the simplest seal variant, the labyrinth seal can be considered the most important non-contact seal type. It offers maximum flexibility in manufacturing as well as a very good sealing performance and is also an inexpensive solution when choosing a seal. As is typical for these non-contact seals, labyrinth seals can be operated almost at the limiting speed of the rolling bearing, depending on the design. There are three main types of labyrinth seals, including an axial, a radial and a self-adjusting version. Self-adjusting labyrinth seals are used, for example, in bearing housings.
Contact seals
Contact seals are seals with a moulded sealing lip made of synthetic rubber that seals against the shaft, housing, inner ring or outer ring. The rubber is vulcanised onto a sheet metal plate. The big advantage of contact seals compared to non-contact seals is their sealing capacity, which is significantly greater. Nevertheless, aspects such as the frictional torque and the temperature increase are also considerably higher with contact seals. Because the sealing lip of the contact seals rubs against the shaft, the permissible circumferential speed depends on the seal type. In addition, the sealing lip must be lightly pre-greased before assembly so that it does not run dry or wear out during the first few minutes of use.
There are manufacturers who have specialised in producing different sealing concepts. This means that there are seals made of various materials (including metal and plastic) and in a wide range of variants that have individual properties in terms of thermal variability and sealing performance.
Examples of contact seals
All seals listed in the table are examples of contact seals, but are also external seals. In the case of external seals, the shaft should be ground free of twists in the contact area of the seal in order to prevent lubricant from being ejected from the bearing.
| Contact seals | ||
| Seal structure | Designation | Sealing properties, design criteria |
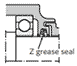 | Z-grease seal |
|
 | V-ring seal |
|
 | Radial shaft seal |
|
 | Felt ring seal |
|
The Z-grease seal, the V-ring seal, the rotary shaft seal and the felt ring seal are all contact seals.
Relief holes for contact seals
All contact seals should have a relief hole to ensure pressure equalisation between the bearing and the bearing environment at all times. This must be placed in such a way that there is no excess pressure in the housing that could result in lubricant leakage. The choice of relief hole should take into account the mounting position of the drive unit to prevent lubricant leakage. During the painting process, it must be ensured that the relief hole is not closed unintentionally. With regard to the radial shaft seal, the permissible circumferential speed for the seal lip should be observed. Furthermore, the installation direction of the rotary shaft seal determines its function. The rotary shaft seal can either prevent ingress of contaminants or the escape of lubricant.
| Seal/material | Permissible peripheral speed m/s V(m/s)= (π×d(mm)×n(r/min))/(60 000) |
Permissible temperature | |
|
Radial shaft seal |
NBR | 16 or less | -25 ~ +120℃ |
| ACM | 26 or less | -15 ~ +150℃ | |
| FKM/ FPM |
32 or less | -30 ~ +200℃ | |
| Z-grease seal | NBR | 6 or less | -25 ~ +120℃ |
| V-ring | NBR | 40 or less | -25 ~ +120℃ |
In the table you will find information on the permissible speed depending on the seal material and temperature.
You may also be interested in
Bearing mounting and the design of surrounding components
Generally speaking, a bearing is only as good as its environment. Who can perform at their best if they don’t feel comfortable in their surroundings?
Bearing units
Characteristics of bearing inserts The bearing insert, which in principle is constructed like a deep groove ball bearing, has a spherical outer ring surface. The
Fit selection
Interference fit, transition fit, clearance fit. You should know and be able to define these three types of fit after reading this article. But before
Lubrication
Nothing works without lubrication: Every bearing runs with grease or oil lubrication, which is the basic prerequisite for avoiding metallic contact of the bearing components,
Rolling bearing types overview
If you have read our article on rolling bearing basics, you probably already know that rolling bearings can basically be divided into two types –
The deep groove ball bearing
Characteristics of deep groove ball bearings In its current form, the deep groove ball bearing has existed – subject to some optimisation – for about




