If you have read our article on rolling bearing basics, you probably already know that rolling bearings can basically be divided into two types – ball bearings and roller bearings.
Ball bearing
Ball bearings are generally characterised by the fact that their rolling elements have the shape of a ball and contact the bearing raceway at one point. When they are loaded, the contact area forms a circle due to elastic deformation. Due to the point contact, the rolling resistance of this type of bearing is low, so the bearings are primarily used in applications with higher speed and lower loads. Normally, their load capacity is not as high as that of roller bearings, however radial ball bearings can support loads in both axial and radial directions.
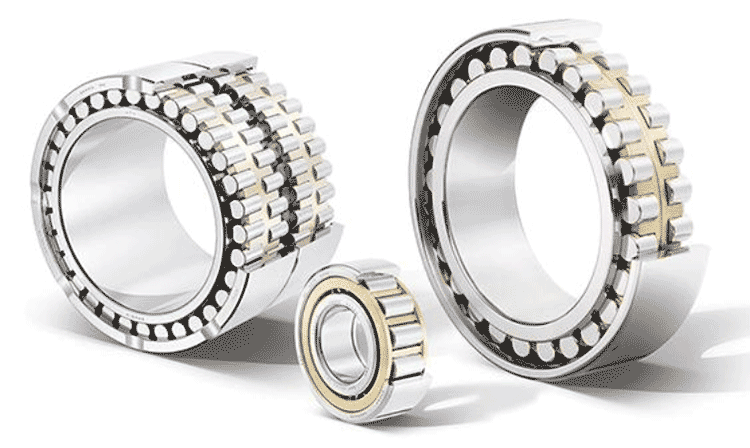


The elongated rolling elements of the roller bearings, here using cylindrical roller bearings as an example, have linear contact with the raceway.
Roller bearing
Roller bearings generally have the opposite characteristics of ball bearings: The contact surface of the loaded rolling elements with the raceway has the shape of a rectangle due to elastic deformation. Line contact leads to a comparatively high frictional torque and higher rigidity. For this reason, roller bearings are more suitable for applications with lower speeds compared to ball bearings. Roller bearings have a high load carrying capacity. With a few exceptions, they mainly support radial loads only.
Ball bearing | Roller bearing |
| Point contact | Line contact |
| Low rolling resistance | High frictional torque |
| Suitable for high speed applications | Applications must have lower speed than ball bearings |
| Lower load capacity | Higher load capacity, high stiffness |
| Load capacity typically possible in radial as well as axial direction | Load capacity in most cases only possible in radial direction |
Where there is light, there is also shadow: Speed and load carrying capacity are important factors in the context of rolling bearings, but they can never be high at the same time.
Ball bearing and roller bearing types
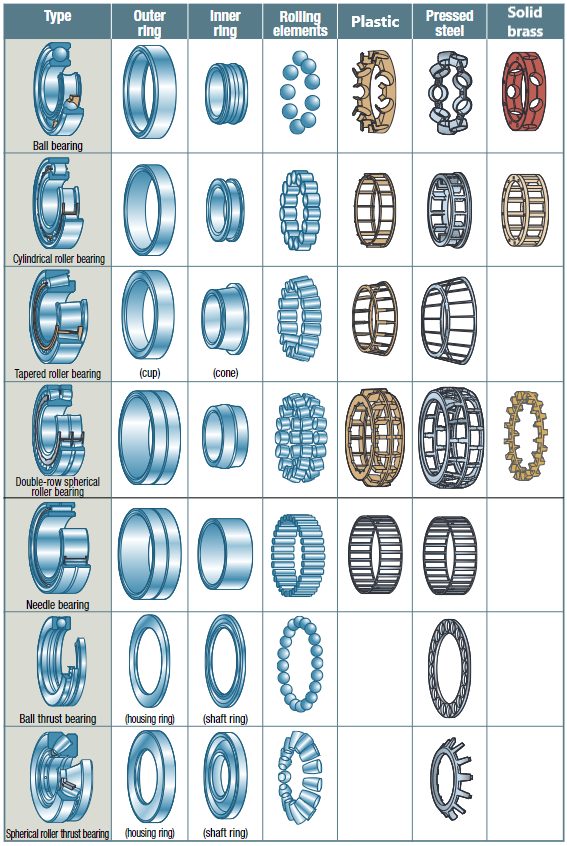
Well-known ball bearing types are deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings and four-point contact bearings. Among the roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings are particularly noteworthy. Other roller bearing types in which the rolling elements have a slightly modified form of a cylindrical roller are, for example, needle roller bearings and tapered roller bearings. In the subchapters of the rolling bearing types section, in-depth information on the individual ball bearing and roller bearing types as well as housing bearings can be found. The main properties of individual bearing types can be viewed in the table as an overview.
| Type | Image | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ball bearing | |||
| Deep groove ball bearing |  |
|
|
| Angular contact ball bearing |  |
| |
| Thrust (axial) deep groove ball bearing |  |
|
|
| Roller bearing | |||
| Cylindrical roller bearing |  |
|
|
| Tapered roller bearing |  |
|
|
| Spherical roller bearing |  |
|
|
| Needle bearing |  |
|
|
In addition to the general advantages and disadvantages of ball bearings or roller bearings, the individual bearing types have specific properties.
This table gives you an overview of the most important types of rolling bearings, including their rolling elements and cage designs.
You may also be interested in
Basics and areas of application
What is a rolling bearing? Would you like to learn more about rolling bearings? Then you’ve come to the right place. But let’s start with
Bearing units
Characteristics of bearing inserts The bearing insert, which in principle is constructed like a deep groove ball bearing, has a spherical outer ring surface. The
Point and line contact
What is meant by “point and line contact”? You may have already heard that rolling bearings can be split into two types. The classification depends
Structure and function
Components of rolling bearings The basics of rolling bearing technology include the structure and function of rolling bearings. To get you started slowly, you will
The cylindrical roller bearing
Characteristics of cylindrical roller bearings Do you remember the characteristic that all roller bearings have in common? We are talking about line contact, which can
The deep groove ball bearing
Characteristics of deep groove ball bearings In its current form, the deep groove ball bearing has existed – subject to some optimisation – for about